
Report Shows How Organisations Are Increasing Investments to Secure Remote Work
21st September 2020
Because of the COVID-19 pandemic, business leaders have had to rapidly change the way their organisations and employees operated particularly as local governments required or recommended employees work from home when and if possible. Under normal circumstances, businesses would make this shift over a long period of time to ensure that their IT infrastructure was prepared to handle such a change. Because of the nature of the pandemic, this shift to telework happened nearly overnight, creating sometimes new security challenges.
In the new 2020 Remote Workforce Cybersecurity Report, Fortinet explores the challenges organisations faced as a result of the shift in remote work and how organisations are planning to secure their remote workforce moving forward. This report, conducted in June 2020, surveyed security leaders across industries—including the public sector—in 17 different countries.
The Sudden Shift to Telework Was Challenging for Most Organizations
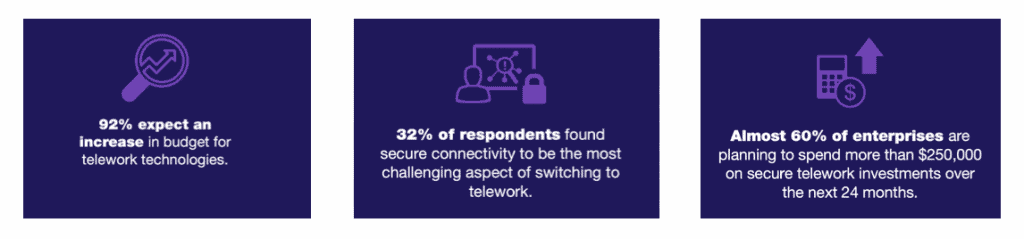
As expected, a rapid shift to a new work paradigm was not easy. Nearly two-thirds of businesses had to transition over half of their workforce to remote work practically overnight. Eighty-three percent of organisations found this transition moderately, very, or extremely challenging. They faced the most significant difficulties when it came to secure connectivity, followed by business continuity assurance and access to business-critical applications.
These challenges are exacerbated by the unprecedented cyber threat activity that has resulted from an increased reliance on personal device usage and the influx of workers outside the corporate network. Cyber adversaries from opportunistic phishers to nation-state actors found numerous ways to exploit the global pandemic, as seen in a recent FortiGuard Labs Global Threat Landscape Report. In fact, 60% of organisations revealed an increase in cybersecurity breach attempts following the transition, while 34% reported actual breaches in their networks.
Enterprises Must Adapt to Secure Telework Long-Term
Given the security challenges above, and the fact that nearly 30% of organisations are expecting more than half of their employees to continue working remotely full-time after the pandemic, security leaders must carefully consider what technology and strategies are required to secure telework well into the future. To ensure the protection of corporate data and assets, organisations must adapt their cybersecurity policies to account for the extension of the network perimeter to the home.
40% of those surveyed spent more on skilled IT workers to support the additional reliance on IT staff to enable security and productivity for employees working from home. Only 40% of organisations had a business continuity plan in place prior to the pandemic. But as a result of the pandemic and the rapid shift to remote work, 32% invested further in this area.
Almost all organisations expect to invest more to secure telework long-term, with nearly 60% of enterprises spending more than $250,000 in secure telework investments in the next 24 months. Moving forward, the majority of enterprises surveyed intend to make unplanned upgrades to their existing systems to secure telework. Many also plan to add new technologies not previously in place.
Additional Investment Areas That Can Maximize Secure Telework Investments
While organisations have made improvements in securing their remote workforces since the beginning of the pandemic, survey data reveals several areas that could be considered opportunities for improving secure remote connectivity. These areas include:
- Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) – The survey revealed that 65% of organisations had VPN solutions in place pre-pandemic, but only 37% of organisations had multi-factor authentication (MFA). While VPNs play an important role in ensuring secure connectivity, they are simply one part of securing access. Therefore, if not already in place, it is recommended that organisations consider integrating MFA into their remote security plans.
- Endpoint Security and Network Access Control (NAC) – 76% and 72% of organisations plan to either upgrade or adopt NAC or endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions respectively. As employees work remotely, organisations face challenges to control the influx of non-trusted devices on their networks to enable remote work, creating new security challenges overnight. By adopting NAC solutions, IT teams get increased visibility and control over the users and devices on their network. EDR solutions deliver advanced, real-time threat protection for endpoints both pre- and post-infection.
- Software-defined Wide-area Networking (SD-WAN) for the Home – 64% of organisations plan to either upgrade or adopt SD-WAN, but specifically for the home office. The critical advantage of extending secure SD-WAN functionality to individual teleworkers, especially super users, is that they can enjoy on-demand remote access as well as dynamically scalable performance regardless of their local network availability.
- Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) – 17% of organisations made investments in SASE prior to the pandemic, and 16% invested in SASE as a result of the pandemic. Still, 58% plan to invest in SASE to some degree going forward. Although SASE is an emerging enterprise strategy, it is increasingly seen as an opportunity to combine network and security functions with WAN capabilities to support the dynamic, secure access needs of today’s organisations.
- Skilled Security Professionals – At the start of the pandemic, only 55% of organisations had enough skilled IT workers in place to support the shift to remote work. And while 73% of organisations stated their intention to invest further in skilled IT workers in the next 24 months, the historical lack of skilled IT security professionals could present a challenge.
Programs like the Fortinet NSE Training Institute’s certification program help teach new skills to, upskill, or reskill security professionals in an effort to reduce the skills shortage. The recent surge in those registering for Fortinet’s training programs is an indicator of the need for trained security professionals. As a result of the transition to remote work, Fortinet made its online training courses free to help businesses combat cyber risks and protect against threats that exploit the COVID-19 pandemic.
Securing Remote Connectivity Well into the Future
Now that organisations have made it through the initial shift to remote work, IT decision makers must plan for the additional investments required to secure telework long-term. There is an opportunity to maximise their investments with cybersecurity platforms designed to provide comprehensive visibility and protection across the entire digital infrastructure, including networked, application, multi-cloud, and mobile environments.

